How to treat high ammonia nitrogen wastewater
Whether it's municipal sewage, or some industrial water, or some aquaculture tailwater. Water contains a large number of ammonia, nitrite and other substances. Ammonia nitrogen has the greatest effect on water quality index. Because there are a lot of proteins and other things in the water, and these proteins are under the action of bacteria. It's converted to ammonia and nitrite. Both ammonia nitrogen and nitrite are substances that can be dissolved into water and are difficult to remove thoroughly with conventional filtration equipment. What do we do with these soluble substances? This involves the treatment of ammonia nitrogen wastewater. Today we will focus on how to treat high ammonia nitrogen wastewater in aquaculture water.
In aquaculture, we feed a large number of fish and shrimp into the aquaculture pond every day. These feeds contain a lot of protein. Under the action of environmental microorganisms, proteins will first break down into small molecules of amino acids. The amino acids are then broken down into soluble ammonia. Ammonia nitrogen under the action of nitrifying bacteria. Further decomposition will turn it into nitrates. In the process. The collaboration of biological bacteria and dissolved oxygen is required. Therefore, this process is a consumptive process. Ammonia nitrogen and nitrite are very toxic to fish and shrimp soluble substances. When nitrite is too high. It will seriously affect the absorption of dissolved oxygen in the water, and then cause the fish and shrimp hypoxia poisoning and death. Therefore, the fishery water quality standards clearly define certain standards for ammonia nitrogen and subsalt in aquaculture water bodies. In general. We believe that the ammonia nitrogen content in the aquaculture water does not exceed 0.2mg per liter. The nitrite content does not exceed 0.02mg per liter. It's a relatively safe concentration. But the feed is constant, and the fish and shrimp are growing every day. As a result, proteins and other nitrogen-containing substances accumulate in the water. Therefore, ammonia nitrogen, nitrite and nitrate are separated from water by certain means. It is a very important task for aquaculture, especially factory aquaculture.
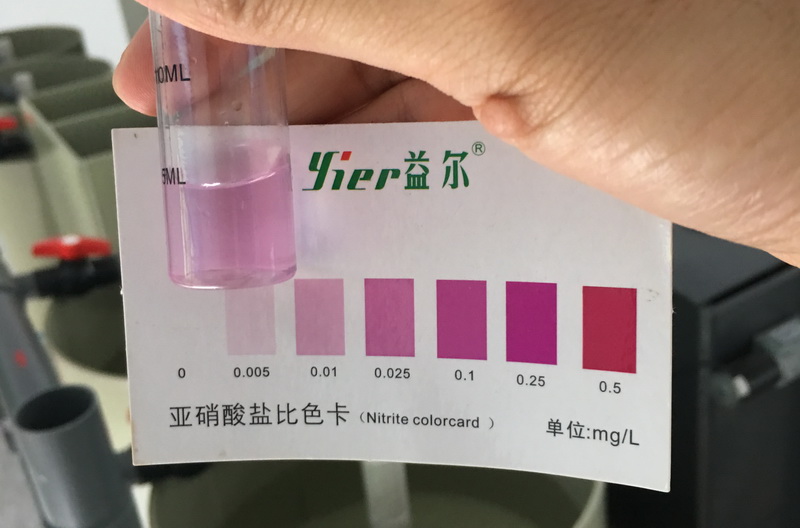
Ammonia nitrogen and nitrite are soluble substances. Therefore, it cannot pass the conventional. Filtration separates them from the water. Below I will introduce several methods of removing ammonia nitrogen from water.
The first recommended method is biofiltration. It is generally suitable for industrial aquaculture water. Factory water aquaculture is a relatively environmentally friendly aquaculture model. Aquaculture wastewater discharge is small. Water after filtration, oxygenation, biochemical treatment and other links. Go back to the breeding pond and reuse it. The breeding density of the unit is higher. The relative indexes of water body are constant. The density of breeding is larger. It is sensitive to the concentration of ammonia nitrogen and nitrite. Therefore, in this case, we recommend to use circulating aquaculture system for water treatment. The treatment method of ammonia nitrogen wastewater. This is done primarily by biofiltration. Biofiltration is the establishment of a biofilter in a recirculating aquaculture system. Put some porous material into a biological filter. Under the condition of maintaining good temperature, pH value and dissolved oxygen, microbial culture is carried out. Common microorganisms are nitrifying bacteria, decomposition bacteria, lactic acid bacteria, denitrifying bacteria. Among them, the bacteria that convert ammonia nitrogen into nitrite and nitrite into nitrate are collectively called nitrifying bacteria. Nitrifying bacteria are a kind of heterotrophic bacteria.
Porous materials generally have a large specific surface area. This facilitates the attachment of biological bacteria. At the same time, some porous materials, such as volcanic stone and coral sand. In favor of biological bacteria reproduction at the same time. It can also regulate water quality. These substances contain some trace elements such as calcium, phosphorus and potassium. The circulating water body can be fine-tuned.
Biofiltration (biofiltration) is one of the most commonly used methods to remove ammonia-nitrogen wastewater from industrial aquaculture. But he also has shortcomings. The disadvantage is that bacteria need a certain period of hanging film. At the same time, the biological filter tank needs a large capacity. Also need water dissolved oxygen, temperature, pH and other indicators to match it. On the scene of factory aquaculture. If the biological filter area is too large. Will reduce the average benefit output of the entire site. Therefore, I think this is not a very ideal method.
 In the past, many farm managers regularly put nitrifying bacteria and other living organisms into the biological filter to promote the rapid conversion of high ammonia nitrogen wastewater into nitrate. But this approach. Often very little. Because the growth and reproduction of nitrifying bacteria need many conditions to cooperate. One of the conditions is not met. The nitrifying bacteria will soon die from competition from other biological bacteria. Can not convert high ammonia nitrogen waste water to nitrate purpose. Therefore, Guangzhou Lanling aquatic technology Co., Ltd. after years of practice. A method has been developed to cultivate native nitrifying bacteria. In the whole process, nitrifying bacteria are no longer injected into water, but the growth factors of digestive bacteria are fully satisfied, so that they can reach a certain concentration in natural water. It is then fed into a circulating water system.
The second ammonia wastewater treatment method is called resin adsorption method. Some resins have been optimally modified. It can absorb ammonia, nitrite and nitrate dissolved in water. Moreover, the characteristic of these resins is that when it adsorbates to saturation, it can be processed by artificial means. Remove ammonia nitrogen or nitrite bound to the resin. And then reuse it. However, the disadvantages of this resin adsorption method are also obvious. That is, the cost of this resin is very high. For hundreds of cubic, thousands of cubic water aquiculture farms. Resin adsorption method is not operable.
In the past, many farm managers regularly put nitrifying bacteria and other living organisms into the biological filter to promote the rapid conversion of high ammonia nitrogen wastewater into nitrate. But this approach. Often very little. Because the growth and reproduction of nitrifying bacteria need many conditions to cooperate. One of the conditions is not met. The nitrifying bacteria will soon die from competition from other biological bacteria. Can not convert high ammonia nitrogen waste water to nitrate purpose. Therefore, Guangzhou Lanling aquatic technology Co., Ltd. after years of practice. A method has been developed to cultivate native nitrifying bacteria. In the whole process, nitrifying bacteria are no longer injected into water, but the growth factors of digestive bacteria are fully satisfied, so that they can reach a certain concentration in natural water. It is then fed into a circulating water system.
The second ammonia wastewater treatment method is called resin adsorption method. Some resins have been optimally modified. It can absorb ammonia, nitrite and nitrate dissolved in water. Moreover, the characteristic of these resins is that when it adsorbates to saturation, it can be processed by artificial means. Remove ammonia nitrogen or nitrite bound to the resin. And then reuse it. However, the disadvantages of this resin adsorption method are also obvious. That is, the cost of this resin is very high. For hundreds of cubic, thousands of cubic water aquiculture farms. Resin adsorption method is not operable.
As a third treatment method for high ammonia nitrogen wastewater, I recommend ozonation. Ozone is a highly oxidizing substance. It is 600 times more oxidizing than chlorine gas. And because it has an oxygen atom that's free, it's very reactive, and it can easily react with something, what we call a REDOX reaction. In the process of recirculating aquaculture. Early procedures remove most of the organic matter from the water. Dissolved ammonia and nitrite can be oxidized by ozone, rapidly turning them into nitrates. Thus reducing the toxicity of the entire water body.
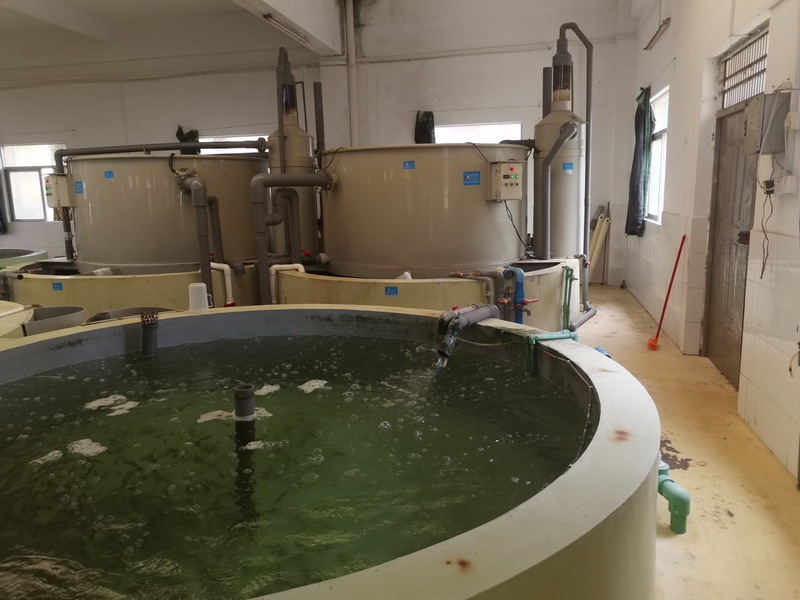

But ozone oxidation also has some disadvantages, that is, the amount of ozone is not easy to control. Ozone is a substance that is difficult to dissolve into water. Therefore, it is a very critical factor to mix the ozone produced by the ozone generator with water in order to achieve the highest utilization efficiency. This means that as much ozone as possible should be dissolved into the water and chemically reacted with ammonia or nitrite in the water. If too much ozone is dissolved into the water, the excess ozone will flow into the aquaculture tank, and it may cause irritation to fish, shrimp or aquatic seedlings, which will cause stress to these aquatic animals. So what's left of ozone is actually harmful. We can treat ozonation as a separate process in the process of operation, especially in the industrial recirculating aquaculture system. So as to avoid ozone residual reflux into the aquaculture tank.
In recent years, Guangzhou Lanling Aquatic Technology Co., Ltd. has done a lot of research on the treatment of aquaculture ammonia nitrogen waste water. We have imported some new type complexing materials from abroad. The ammonia nitrogen and nitrite in water can be quickly adsorbed and complexed. To make less or less toxic. Our experiments show that. The complexing agent was released into the water at a rate of 30mg of nitrite per liter. Even at high concentrations, nitrite is not toxic to aquatic seedlings. This kind of complexing agent is suitable for some emergency situations. But this complexing agent also has its own disadvantages, that is, it is also easy to react with organic compounds in the water. Therefore, when complexing agents are used to react with nitrite and ammonia nitrogen, it is necessary to ensure that the concentration of insoluble organic matter in the water is minimized. In other words. Aquaculture water should be treated in the early stage, and it should be fully filtered, so that the solid suspended matter and COD in the water can be reduced as much as possible. In this way, the amount of complexing agent can be reduced as much as possible.




